Highlights
In the past, we used to put much emphasis on the analysis and evaluation of traffic safety and its rescue in the field of traffic safety. Since two or three years ago, the study on traffic safety has been focused on whether the risk can be controlled or not. Therefore, many experts have turned to risk management from design, evaluation, emergency management of the traffic safety. This is an inevitable trend.
My research is mainly focused on the traffic safety and traffic design. Since 2010, we have also found that many events in fact can be avoided through risk control. It can be better and effectively reduced for the occurrence of possible events. Our teams have been involved in the study of risk management. We have spent a lot of efforts in this regard and have undertaken a number of projects as well.
Risk management differs greatly with emergency management. In the past, management approaches were only taken after incidents occurred, i.e., emergency rescue. It aimed to reduce the loss caused by the incident. Risk management is focused much more on events which have not occurred yet, but we observe what factors will possibly cause the event to occur and what the possible consequences are. We pay much attention on prevention and control in order to reduce accidents as much as possible. A typical example is the stampede near the Bund in Shanghai, which could be controlled if we had performed properly in risk management. Because, that the risk was predictable. In fact, if this risk had been predicted, we could have provided better measures for prevention and control.
For example, if your car tires may be a bit worn, this is a hidden danger. But, if you keep the car in the garage, instead of driving it onto the road, there is no risk and there will be no accident. However, if the car is driven out of the garage onto the road, the hidden danger becomes a risk, as the tire may explode, resulting in the vehicle out of control. Once an incident occurs, it will have consequences, resulting in a disaster, which is a whole process of the event. So what is the key task for us to complete for risk prevention and control? First, hidden dangers should be checked to make sure that the probability of hidden danger becoming a risk can be reduced. Second, once the hidden danger becomes a risk, then there is no doubt that we have to control the hidden danger from being a risk. After that incident occurs again, we will not let it become a disaster. This is the whole process of risk management.
Road traffic safety is the main subject of the entire traffic safety. The vast majority of these accidents occur on the road. After years of hard work, traffic accident mortality decreases year by year in our country, which is a good achievement. But, if compared to the developed countries or other countries, it leaves much to do for risk management.

Then, what is the risk? What is the basic feature of risk management? It is full of uncertainty. It is uncertain for a bad tire to explode. Even if it explodes, when no other cars are around, it will not cause very serious consequences. So, its uncertainty is tremendous. Our mission is to direct and control the coordination activities of various organizations to ensure that these hidden risks and the probability of occurrence of the incident getting lower and lower. The whole process includes risk identification, risk analysis, risk assessment and risk response. Tire checking is a kind of risk identification, which is a very important factor in the risk source. Risk analysis is to analyze whether the explosion may occur, if the tire is not good for traffic. Risk assessment is to assume certain events, including the tire explosion, the vehicle out of control, the collision and the rollover. There is no doubt that the response should be started from the risk source, and then make analysis to ensure that the risk source can be controlled.
In general, the event consequence and the probability of event occurrence are combined to indicate the risk. The stampede near the Bund abovementioned is an event that would likely occur. It is the event consequence and the probability of event occurrence. Once the population density reaches a certain extent, it will become a very dangerous risk.
Basic features of the risk are uncertain, dual, futuristic, eventful, targeted, objective and subjective integrated and so on. The trouble of vehicle brake is a hidden danger. After the vehicle entering the traffic flow, there is a risk, including vehicle out of control and rear-end collision. Hidden dangers are the source of unsafety which could cause some undesirable consequences. An accident is the event which causes damage to the life, property, or environment. This is the process of events from hidden dangers to accidents.

Risk management should solve a series of scientific problems. What will go wrong? This is the hidden danger that we talk about. What is the possibility of error? This is the analysis of risk, and it does not mean that an event or an accident will occur. What will be the result? What shall we do, if this risk exists? What are sources of the failure? They are hardware failure, software failure, organization failure and human failure.
What is the purpose of risk management? The answer is very clear. It is to control the risk source, and control hidden dangers. What options are available? Can they be weighed against costs, benefits and risks? What is the impact of current management decisions on future options? These questions can be answered by experience and advice of the experts.
Risk analysis is qualitative and preliminary analysis. For example, what will happen after a car is driven into the traffic flow? Risk assessment is how much disaster will occur after the accident, such as collision, major accident, burning, or explosion. There is a difference between quantitative and qualitative. The risk analysis is much more qualitative at macro level, while the risk assessment is much more quantitative at micro level. It should be studied based on the specific data analysis. This process is the process for risk management, which is the preliminary judgment of risks. Possible risks can be figured out by the definition of some rules for risks. These risks can be analyzed after they are listed. What kind of consequences may occur? These consequences are qualitative and macroscopic. Finally, the risk assessment is to analyze the probability of event occurrence caused by the risk, and what impact of this probability caused. This table in red, yellow and green is a very important table in risk management. When the traffic state is in green, it shows safe without much problem. When it is in yellow, it shows that this area has certain degree of risk. When it is in red, it shows that the probability of risk has been great.
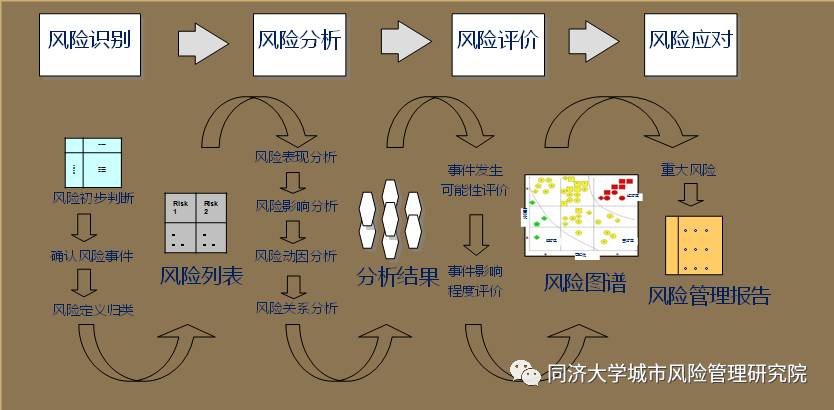
This sort of the table is often made in implementing risk management. The most significant thing is that after combining large amount of data, the traffic status can be figured out. Where the condition point locates, it shows what the status it is. Take the S32 chain crash and the stampede near the Bund for example, if a lot of data had been put into our analysis system, we would have known much clearer about the responding measures, based on the analysis of big data. Therefore, the importance of strengthening risk management and control is self-evident.
The priority task of risk identification is to identify potential events, risk sources, and risk reasons, so as to find out hidden dangers. The second task is to identify the consequences, the nature and the impact scope of risks. This is the aforesaid risk analysis and evaluation, to find out possible measures for management and control, which is the key task for risk identification. One very important thing is that how great the probability is, when it occurs, and where it probably locates. All these can be modelled to make probabilistic analysis based on large amounts of data. This probabilistic analysis is based on our past experience and the evaluation of experts, which can be qualitative or quantitative. In general, it is suggested to take quantitative measures. By means of big data, approximate results, including consequences, status, impact scope and severity of the risk, can be given after the information from all aspects has been put into the analysis software. The effectiveness and efficiency of control measures can be analyzed. All these can be implemented through the analysis system and the expert system. It is unnecessarily to make artificial subjective judgments.
The evaluation should be quantitative, but as microscopic as possible. First, the overall consequences of the risk-induced event should be defined, and it is generally called the “C-criterion”. The criterion to be adopted may vary based on different traffic conditions, different features, and different operating modes. The overall probability of risk occurrence can be defined. As the map in green, yellow and red aforesaid, it can be extended to obtain several levels. All levels, such as level one, level two, level three and level four, are shown respectively in red, yellow, orange and blue. The state level of these accidents can be obtained by quantitative measures.
The primary means of response is to prevent the risk first. When we realize that there is a risk, we immediately make risk diversification, that is, the bigger risk is divided into several smaller ones. Despite the large amount of risk, they are smaller. Then, small risks are controlled to avoid them from occurring. When the smaller risk occurs, it can be converted, so as to avoid the risk from occurring in the end.
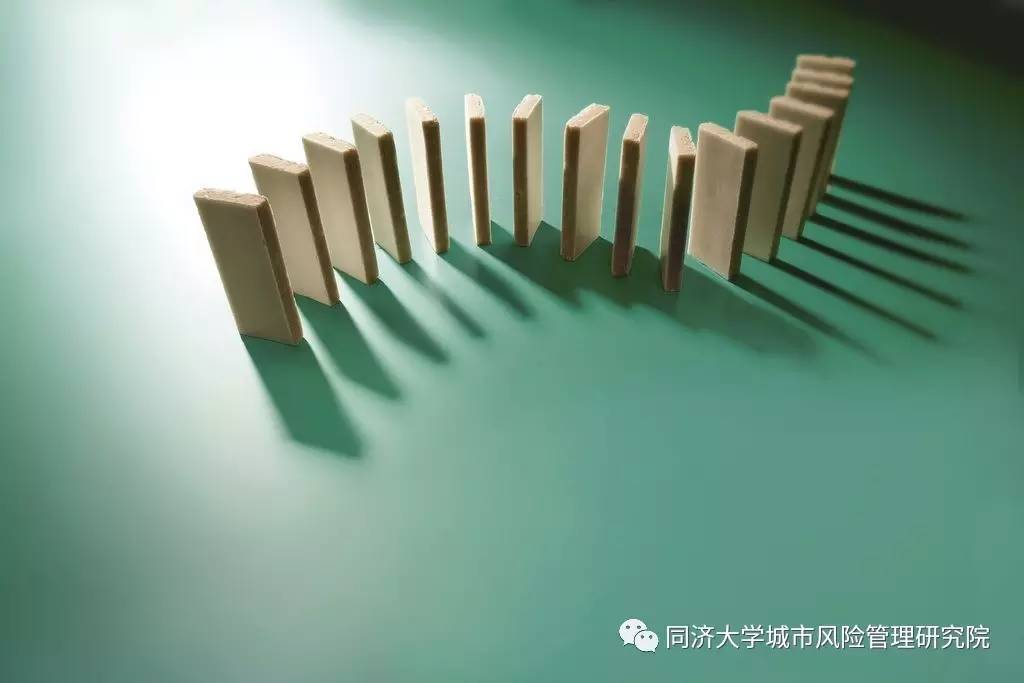
There are two theories on risk management. The first is the domino theory, and in fact, the occurrence of risk is caused by domino effects. Social environment creates a source of danger, but due to human negligence, the danger is uncontrolled or insufficiently controlled, which leads to unsafe behavior, and in turn causes an accident. If it is not properly managed after the accident, it will become an injury incident. The incident aforesaid is not equal to the disaster. The hidden danger does not represent the risk, and the risk does not represent the event. We have to implement risk management for each link, starting from the hidden dangers. If we perform properly, one of the dominoes can be knocked down, and the final event of injury will not happen. This is a very important theory for risk management. If this theory is perfectly mastered, we will have all means to complete the task for each link.

The impact of S32 chain collision events is still significant. For one thing, it is on the highway, and for the other, it is the sudden burst of agglomerate fog. As agglomerate fog has a feature, which will not be noticed when you drive slowly, it will make you invisible in a blink of an eye. We all have this experience when we drive on the highway. Currently, it is very hard for us to detect it, due to the lack of fog monitoring and early warning. There are so many highways in our country that it is very difficult to detect each section of the highway. Here is a case in the United States. In Florida, there is a 10 km long bridge, and a policewoman drove into the fence and fell into the sea due to agglomerate fog. From that on, all the bridges were fitted with agglomerate fog predictors. Since then, there has not been any accident caused by the agglomerate fog.
In the case of S32, it was because the speed of vehicles was too fast and the distance between vehicles was insufficient, which caused a large number of rear-end collision. So, the problem is whether this link can be controlled or not. We believe that it can be controlled, though it is very difficult, because of lacking detectors.

Another theory for risk management is energy release. Here is a very simple case. As a couple lived together in a house, they would have a heated quarrel after several smaller quarrels accumulated due to a variety of daily trifles. Then the energy released. A peaceful life returned for a short period of the time after the heated quarrel. However, they would have a heated quarrel again after smaller quarrels accumulated as before. After the heated quarrel, they would finally be peaceful once again. This is a common phenomenon in life, and this is the same as to the risk management. Then, how can the energy release? The energy release is to control the disaster. The most important thing to do is to prevent the accumulation of energy, for it is much more difficult to deal with after it is aggregated. So, what shall we do if it has been accumulated?
We shall reduce the accumulation of energy. For example, the couple should often communicate peacefully with each other. Assuming that the energy has been accumulated, it would diffuse. We should slow it down, or isolate those vulnerable objects.
There is one more theory called track-cross theory, which is commonly known. This is due to lack of management. It is caused by objects, as well as by people. Objects are in unsafety states, so they are the source of accident and damage. People have unsafe behaviors, so they are the perpetrators and victims. As a result, an accident will occur. In fact, we are able to control any of the links abovementioned.

Author: Lu Jian, Dean of the School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Tongji University.

